Climatic Data (Mediterranean, Nestos River Catchment)
Recent projections by both general circulation models (GCMs) and regional climate models (RCMs) show that future climate will be characterized by monthly net rainfall decrease during winter and potential evapotranspiration increase during summer due to global warming. All expected Climate Change (CC) scenarios as defined by Intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change (IPCC) 5 th Assessment Report (AR5; Allen et al., 2014) will induce a permanent stress on surface/subsurface water levels due to higher demands coupled to water resources shortage. It is also expected that the Mediterranean region will be among the areas that will be most affected by CC (Cramer et al., 2018).
Data from RCM implementations driven by output of GCM simulations were be used, in order to provide input for the Hydrological and Maritime Hydrodynamic Regional Circulation Models. These types of Climatic Data were based on the Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) approach adopted by the IPCC-AR5 (Allen et al., 2014). Two out of the four RCP’s selected for climate modeling and research (RCP2.6, RCP4.5, RCP6 and RCP8.5) were used in the present study, namely RCP4.5 and RCP8.5. The first one describes a possible climate future that depends on “modest” estimations about greenhouse gases emissions in coming years, while the latter poses a “worst case scenario” among the four RCP’s.
- RCP4.5 and RCP6.0 is an intermediate stabilization pathway in which radiative forcing is stabilized at approximately 4.5 W/m2 after 2100 (assuming constant concentrations after 2150).
- RCP8.5 takes into account radiative forcing that reach >8.5 W/m2 by 2100 and continue to rise for some amount of time (assuming constant emissions after 2100 and constant concentrations after 2250).
The aforementioned data were downloaded from the MED-CORDEX database (www.medcordex.eu). MED-CORDEX is a coordinated contribution to CORDEX (COordinated Regional Climate Downscaling Experiment), dedicated to the Mediterranean. MED-CORDEX is supported by HyMeX (https://www.hymex.org/) and MedCLIVAR (http://www.medclivar.eu/) international programs.
The grid resolution of the selected MED-CORDEX sub-domain data (MED-44) is set to 0.44 degree by 0.44 degree for the RCMs using a rotated pole system, where the model operates over an equatorial domain with a quasi-uniform resolution of approximately 50 km.
The original MED-44 data were further processed by the means of the CDO (Climate Data Operators) tool set (https://code.mpimet.mpg.de/projects/cdo/), in order to match the requirements of the study’s simulations and validation. The data coordinates were transformed from the original rotated-pole coordinate system to a regular longitude-latitude one. Subsequently, they were cropped and interpolated to the extents and resolution of the simulations’ desired domains.
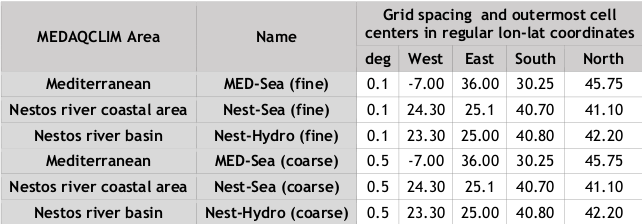
Table MEDAQCLIM MED-44 CORDEX study domains geographic specifications
| MEDAQCLIM Area | Name | Grid spacing and outermost cell
centers in regular lon-lat coordinates |
||||
| deg | West | East | South | North | ||
| Mediterranean | MED-Sea (fine) | 0.1 | -7.00 | 36.00 | 30.25 | 45.75 |
| Nestos river coastal area | Nest-Sea (fine) | 0.1 | 24.30 | 25.1 | 40.70 | 41.10 |
| Nestos river basin | Nest-Hydro (fine) | 0.1 | 23.30 | 25.00 | 40.80 | 42.20 |
| Mediterranean | MED-Sea (coarse) | 0.5 | -7.00 | 36.00 | 30.25 | 45.75 |
| Nestos river coastal area | Nest-Sea (coarse) | 0.5 | 24.30 | 25.1 | 40.70 | 41.10 |
| Nestos river basin | Nest-Hydro (coarse) | 0.5 | 23.30 | 25.00 | 40.80 | 42.20 |
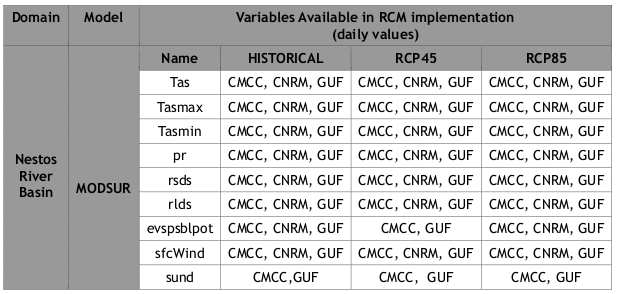
The atmospheric parameters used as forcing of the hydrological/hydrodynamic models consist of wind (velocity and direction) and atmospheric pressure fields, together with temperature and precipitation by three high-resolution RCMs, developed and implemented in three institutions in the framework of the MED-CORDEX initiative (Ruti et al., 2016), namely:
1) CMCC (https://www.cmcc.it/models/cmcc-med),
2) CNRM (https://www.umr-cnrm.fr/spip.php?article1094&lang=en), and
3) GUF (http://www.goethe-university-frankfurt.de/75364063/)
The respective implemented RCMs are:
- CMCC-CCLM4-8-19 v.1 (https://www.pik-potsdam.de/research/climate- resilience/models/cclm)
- CNRM-ALADIN52 v.1
- GUF-CCLM-NEMO4-8-18 v.1
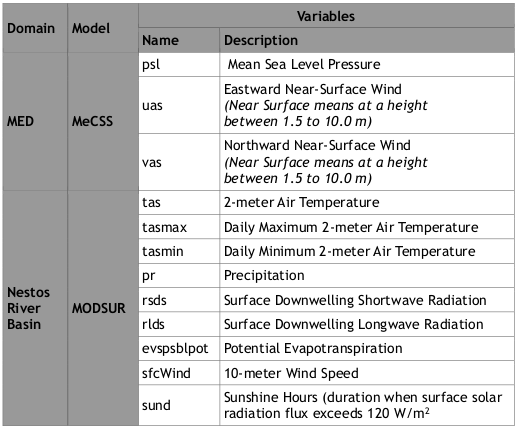
Table MED-CORDEX climatic variable description and names within MEDAQCLIM
| Domain | Model | Variables | |
| Name | Description | ||
| MED | MeCSS | psl | Mean Sea Level Pressure |
| uas | Eastward Near-Surface Wind
(Near Surface means at a height between 1.5 to 10.0 m) |
||
| vas | Northward Near-Surface Wind
(Near Surface means at a height between 1.5 to 10.0 m) |
||
| Nestos
River Basin |
MODSUR | tas | 2-meter Air Temperature |
| tasmax | Daily Maximum 2-meter Air Temperature | ||
| tasmin | Daily Minimum 2-meter Air Temperature | ||
| pr | Precipitation | ||
| rsds | Surface Downwelling Shortwave Radiation | ||
| rlds | Surface Downwelling Longwave Radiation | ||
| evspsblpot | Potential Evapotranspiration | ||
| sfcWind | 10-meter Wind Speed | ||
| sund | Sunshine Hours (duration when surface solar
radiation flux exceeds 120 W/m2 |
||
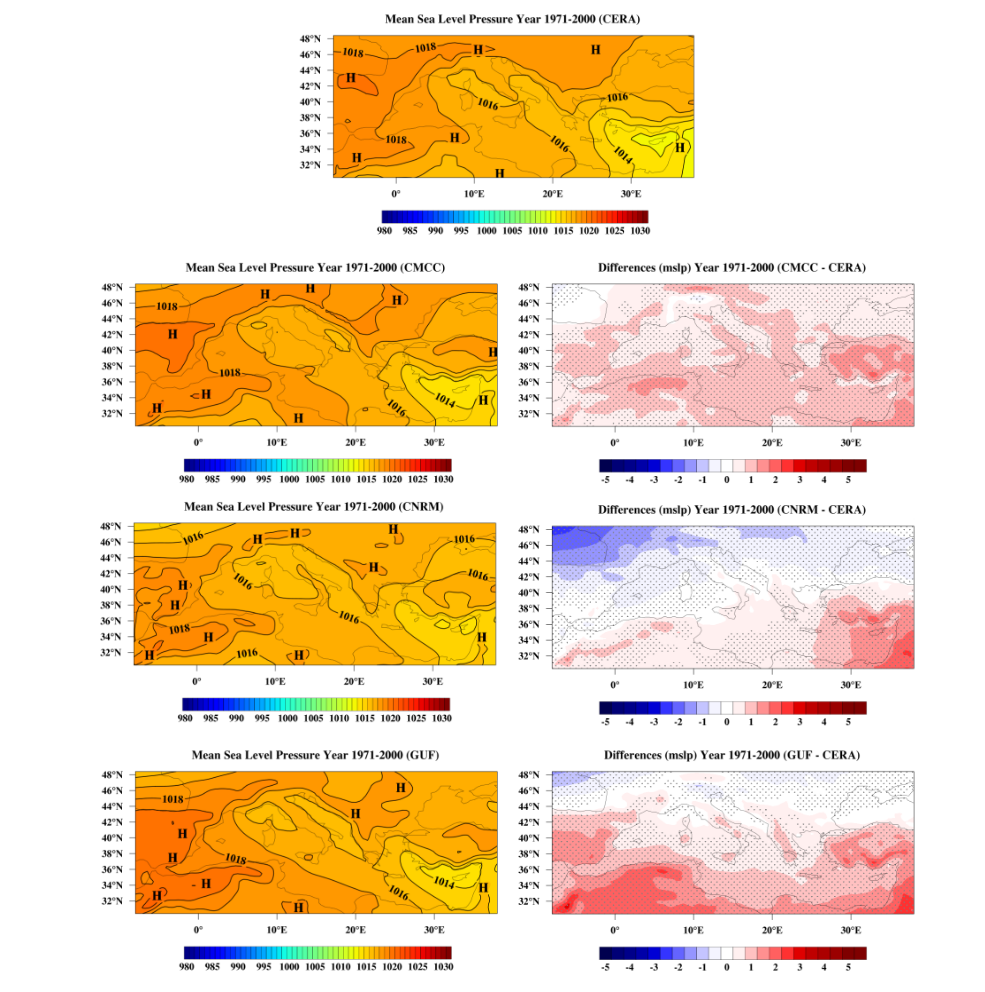
Both the original MED-CORDEX, as well as the post-processed climatic data underwent a validation process, before being used as input of the hydrodynamic and hydrological models. The process was carried out for the historical period of simulations, i.e. the Reference Period 1971-2005 for the Control run simulations, and MED-CORDEX data were compared against CERA (Coupled ECMWF Re-Analysis; https://www.ecmwf.int/en/research/projects/cera) data. Produced temperature and precipitation patterns by RCMs of the MED-CORDEX are well-assessed by recent validation studies in existing literature. Therefore the fields of implementation covered the entire Mediterranean basin and referred only to SLP and winds, as:
(i) these parameters were previously not covered by the literature on MED-CORDEX datasets validations
(ii) they are crucial forcing drivers for large-scale maritime hydrodynamic simulations in the Mediterranean Sea.