Storm Surge Data (Mediterranean)
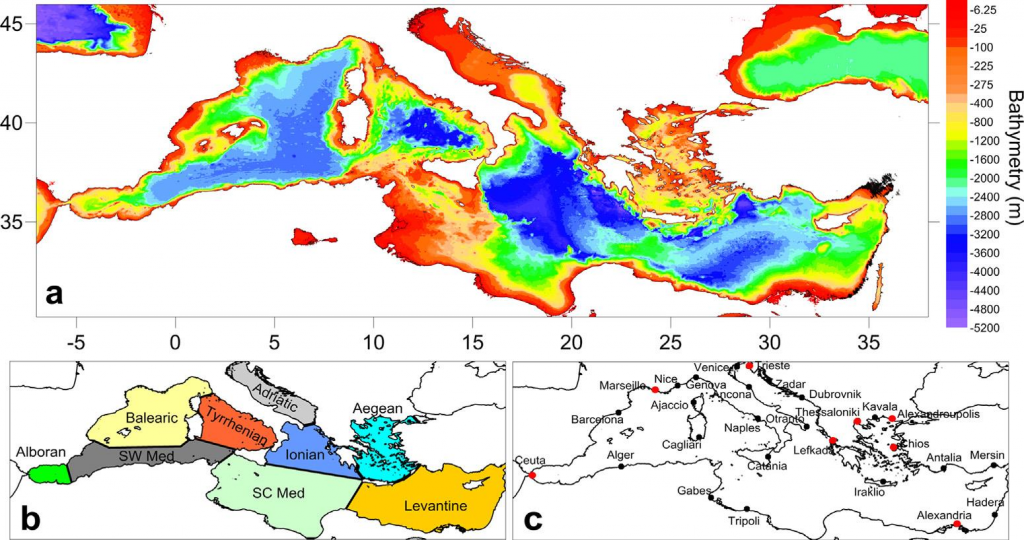
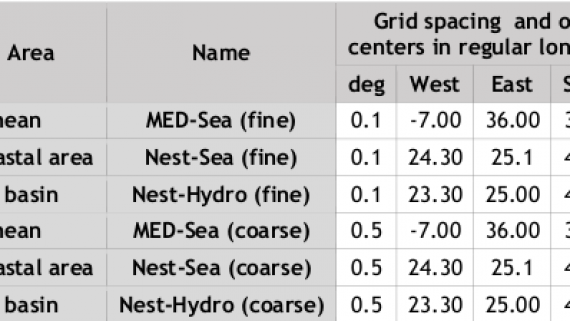
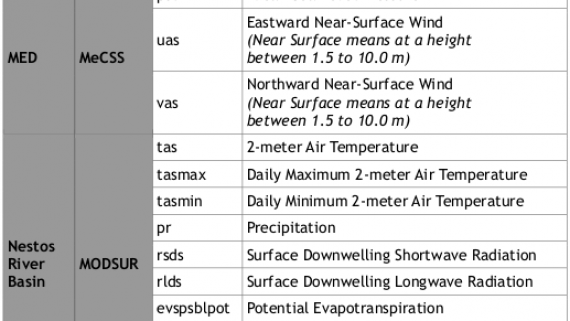
The Mediterranean Climate Storm Surge (MeCSS) model (Androulidakis et al., 2015; Makris et al., 2015) is based on the HiReSS (High Resolution Storm Surge) model (Makris et al., 2019). It is a two-dimensional horizontal hydrodynamic model that solves the depth-averaged shallow water equations for the barotropic mode of circulation (De Vries et al., 1995; Krestenitis et al., 2011) and is used to calculate the sea level variations and depth-integrated currents for the entire Mediterranean basin on a 1/10°×1/10° horizontal grid (Trifonova et al., 2012; Villatoro et al., 2014; Androulidakis et al., 2015; Makris et al., 2015; 2016; 2018). The atmospheric forcing, namely the winds at 10 m elevation from MSL and the SLP fields, are provided by several climate models of the MED-CORDEX database for the entire study period (1971-2100).
HiReSS model can simulate evolution of SSH and barotropic (depth-integrated) sea currents, U and V in shallow coastal shelves. Essentially, it can simulate the effects of storm surges, induced by atmospheric weather conditions, particularly due to the effect of SLP and winds that occur over a marine water body during high and low barometric systems (Krestenitis et al., 2015).
HiReSS/MeCSS model has been developed since the 1990s from members of the Laboratory of Maritime Engineering of AUTh; it has been calibrated, validated, and applied under several circumstances both for short-term forecasting and long-term estimation of SSH in coastal zones of the Mediterranean, Black, Aegean and Ionian Seas (Androulidakis et al., 2015; Krestenitis et al., 2011; 2014; 2015a; 2015b; 2017; Makris et al., 2015; 2016; 2017; 2018; 2019). All computations are executed on an ortho-regular staggered Cartesian grid of the Arakawa-C type, with orthogonal elements with changing dimensions, due to a fixed spatial discretization step of spherical coordinates (geographic longitudes and latitudes, dλ and dφ). The finite differences method (FDM) is used as a discretization technique and an integration approach. It is noted that the typical dimension of the computational grid cells in the Mediterranean region corresponds to dx, dy ≈ 10 Km. HiReSS/MeCSS model takes into account the following physical processes:
- The effects of the barometric pressure gradient causing the variations of the sea level (inverse barometer effect) SSH
- The effect of the wind field (velocity vector field: intensity and direction) patterns on SSH variation.
- The effect of friction on the seabed based on the bottom roughness, bathymetry and shoreline morphology
- The effect of internal shear stresses – frictional forces (in the form of turbulent diffusion).
- The effect of tidal currents on the SSH variations from MSL, based on the static model of astronomical tides by Schwiderski (1980).
- The geostrophic effect due to the Coriolis force acting on large water masses driven by regional hydrodynamic circulation.